Spring的优点
性能好、易于测试、代码可重用高。
Spring,是轻量级的框架,其基础版本只有2MB左右的大小。
Spring框架的核心特性是可以用于开发任何Java应用程序,但是在JavaEE 平台上构建web应用程序是需要扩展的。
Spring框架的目标是使J2EE开发变得更容易使用,通过启用基于POJO编程模型来促进良好的编程实践。
思想:例如在jdbc中实现事务控制,无法实现代码的封装,因为使用jdbc控制事务是面向对象的思想,操作事务的提交、事务的回滚是分布在业务执行过程不同条件下的;而Sping的声明式事务是基于AOP面向切面的编程思想,
Spring Framework
Spring基础框架,可以视为Spring基础设施,基本上任何其他Spring项目都是以Spring Framework为基础的。
Spring Framework特性
·非侵入式:
使用Spring Framework开发应用程序时,Spring对应用程序本身的结构影响非常小。对领域模型可以做到零污染;
对功能性组件也只需要使用几个简单的注解进行标记,完全不会破坏原有结构,反而能将组件结构进一步简化。
这就使得基于Spring Framework开发应用程序时结构清晰、简洁优雅。
·控制反转IOC——Inversion of Control,翻转资源获取方向。把自己创建资源、向环境索取资源变成环境将资源准备好,我们享受资源注入。
·面向切面编程:AOP——Aspect Oriented Programming,在不修改源代码的基础上增强代码功能。
·容器:
Spring IOC是一个容器,因为它包含并且管理组件对象的生命周期。组件享受到了容器化的管理,替程序员屏蔽了组件创建过程中的大量细节,极大的降低了使用门槛,大幅度提高了开发效率。
·组件化:
Spring实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用。在Spring中可以使用XML和Java注解组合这些对象。这使得我们可以基于一个个功能明确、边界清晰的组件有条不紊的搭建超大型复杂应用系统。
·声明式:
很多以前需要编写代码才能实现的功能,现在只需要声明需求即可由框架代为实现。
·一站式:
在IOC和AOP的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库。而且Spring旗下的项目已经覆盖了广泛领域,很多方面的功能性需求可以在Spring Framework的基础上全部使用Spring,来实现。获取IOC,通过IOC获取管理的对象案例
假如新建一个空项目 -> 要实现案例目标,获取IOC容器中的对象 -> 最基础的实现方式,用配置文件的方式,所以要新建配置文件,在resource目录下右键新建xml,如果idea右键菜单栏中没有Spring配置的xml可选项,是因为pom中还未引入spring-context的Dependency
导入maven坐标如下:spring-context 5.2.10.RELEASE稳定版
<dependencies>
< !--基于Maven依赖传递性,导入spring-context依赖即可导入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</ dependencies>1、首先配置对象到IOC容器中,有xml和注解两种方式
xml: 在Spring的xml配置文件,名字约定俗成叫applicationContext.xml,在配置文件中使用bean标签,配置id属性、class属性
<bean id="xxxx" class="全类名"></bean>注解:@Component @Controller @Service @Repository @RestControler更多详细
2、测试用例
public class HelloWorld(){
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello world!");
}
}@Test
public void test(){
//获取IoC容器
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取IoC容器中的bean
HelloWorld helloworld = (HelloWorld)ioc.getBean("helloworld");
helloworld.sayHello();Spring获取bean的三种方式
1、通过name获取
2、通过class type获取
3、同时通过name和type获取
如果组件类实现了接口,根据接口类型可以获取bean吗?
可以,前提是bean唯一
如果一个接口有多个实现类,这些实现类都配置了bean,根据接口类型可以获取bean吗?
不行,因为bean不唯—依赖注入之setter注入
如我们将对象注入Spring容器中时,可以通过对象属性的getter()为属性设置属性值
如实际配置如下:可以为Student类中的属性设置属性值
<bean id="studentTwo" class="com.hlongliu.spring.pojo.Student">
<property name="sid" value="1001"></property>
<property name="sname" value="张三"></property>
<property name="age" value="23"></property>
<property name="gender" value="男"></property>
</bean>依赖注入之构造器注入
如 实际配置如下:
<bean id="studentThree" class="com.hlongliu.spring.pojo.Student">
<constructor-arg value="1002"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="李四"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="24"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="女" name="gender"></constructor-arg>
</bean>代理模式场景
public class CalculatorImpl implements calculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j){
System.out.println(日志,方法: add,参数:"+i+","+j);
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("方法内部,result: "+result);
system.out.println("日志,方法:add,结果:"+result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("日志,方法: sub,参数:"+i+","+j);
int result - i - j;
System.out.println("方法内部,result: "+result);
system.out.println("日志,方法:sub,结果:"+result);
return result;
}
}①现有代码缺陷
针对带日志功能的实现类,我们发现有如下缺陷:
·对核心业务功能有干扰,导致程序员在开发核心业务功能时分散了精力
·附加功能分散在各个业务功能方法中,不利于统一维护
②解决思路
解决这两个问题,核心就是:解耦。我们需要把附加功能从业务功能代码中抽取出来。
③困难
解决问题的困难:要抽取的代码在方法内部,靠以前把子类中的重复代码抽取到父类的方式没法解决。所以需要引入新的技术。
代理模式
概念:二十三种设计模式中的一种,属于结构型模式。它的作用就是通过提供一个代理类,让我们在调用目标方法的时候,不再是直接对目标方法进行调用,而是通过代理类间接调用。让不属于目标方法核心逻辑的代码从目标方法中剥离出来一一解耦。调用目标方法时先调用代理对象的方法,减少对目标方法的调用和打扰,同时让附加功能能够集中在一起也有利于统一维护。
静态代理
创建静态代理类
public class CalculatorStaticProxy implements Calculator {
//将被代理的目标对象声明为成员变量
private Calculator target;
public CalculatorStaticProxy(Calculator target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public int add(int i, int j){
//附加功能由代理类中的代理方法来实现
System.out.println("[日志] add 方法开始了,参数是:" +i + ","+ j);
//通过目标对象来实现核心业务逻辑
int addResult = target.add(i,j);
System.out.println(" [日志] add方法结束了,结果是: " + addResult);
return addResult;
}
}静态代理确实实现了解耦,但是由于代码都写死了,完全不具备任何的灵活性。就拿日志功能来说,将来其他地方也需要附加日志,那还得再声明更多个静态代理类,那就产生了大星重复的代码,日志功能还是分散的,没有统一管理。
提出进一步的需求:将日志功能集中到一个代理类中,将来有任何日志需求,都通过这一个代理类来实现。这就需要使用动态代理技术了。
动态代理
动态代理有两种:
1、jdk动态代理,要求必须有接口,最终生成的代理类和目标类实现相同的接口在com.sun.proxy包下,类名为$proxy2
2、cglib动态代理,最终生成的代理类会继承目标类,并且和目标类在相同的包下
/**
*目标类接口
*/
public interface Calculator{
int add(int i, int j);
int sub(int i, int j);
}
/**
*目标类
*/
public class CalculatorImpl implments Calculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j){
return i+j;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j){
return i-j;
}
}
/** 动态代理核心
*生产代理对象
*/
public class GenerateProxy(){
private Object target;
public GenerateProxy(Object target){
this.target = target;
}
public Object getProxy(){
/**
*newProxyInstance():创建一个代理实例
*共有三个参数
* ClassLoad 类加载器 Class<?>[] 目标对象
*/
ClassLoad classLoad = this.getClass().getClassLoad();
Class<?>[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterface();
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler(){
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//proxy代表代理对象,method代表要执行的方法,args代表执行方法的参数
Object result = method.invoke(target,args);
return result;
}
}
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoad,interfaces,h);
}
}
/**
*测试
*/
public class ProxyTest{
@Test
public void testProxy(){
GenerateProxy generateProxy = new GenerateProxy(new CalculatorImpl());
Calculator proxy = (Calculator)generateProxy.getProxy();
proxy.add(1,2);
}
}
使用Maven快速创建基础Java项目,不选择骨架
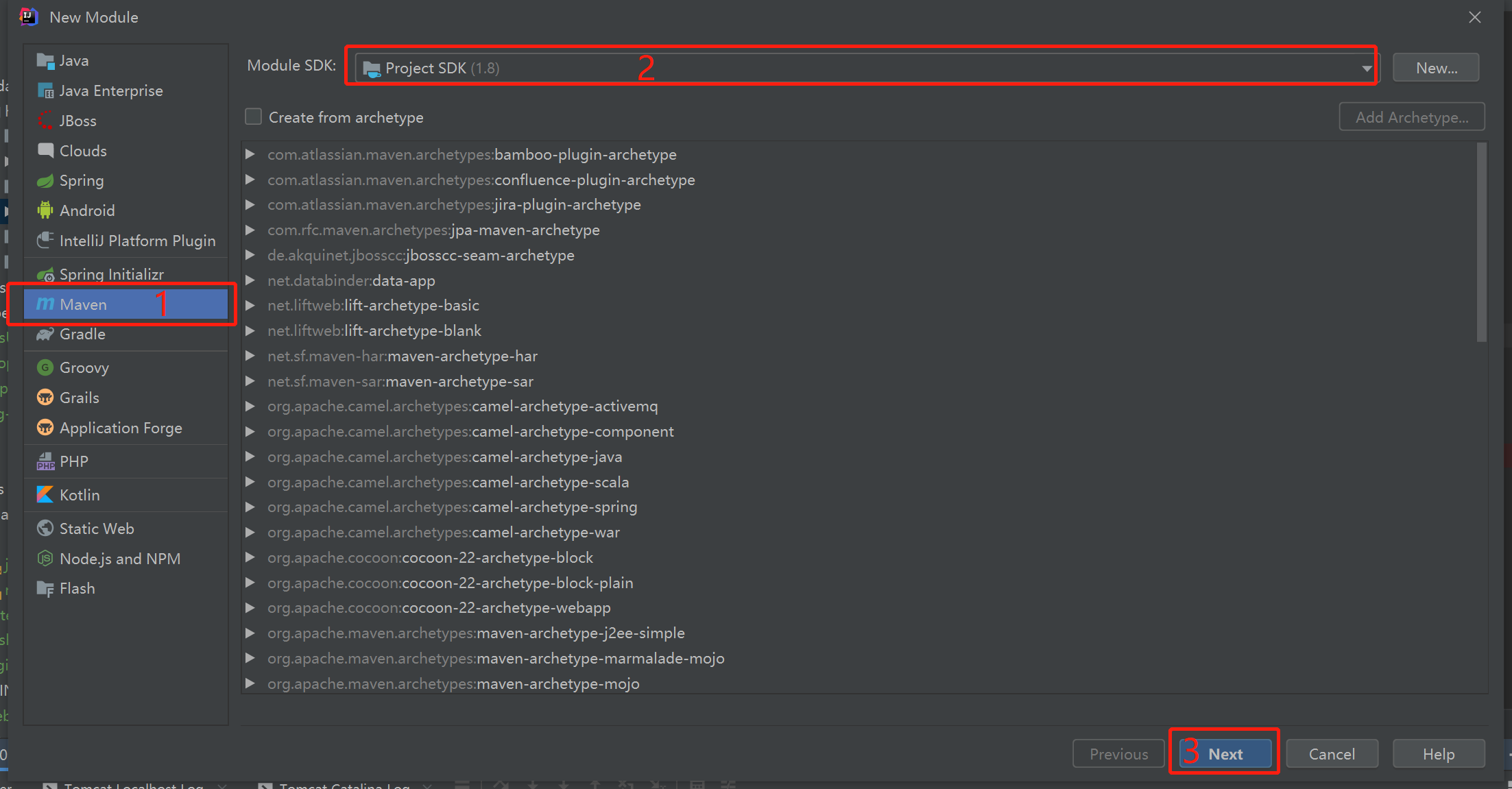
设置项目基本信息
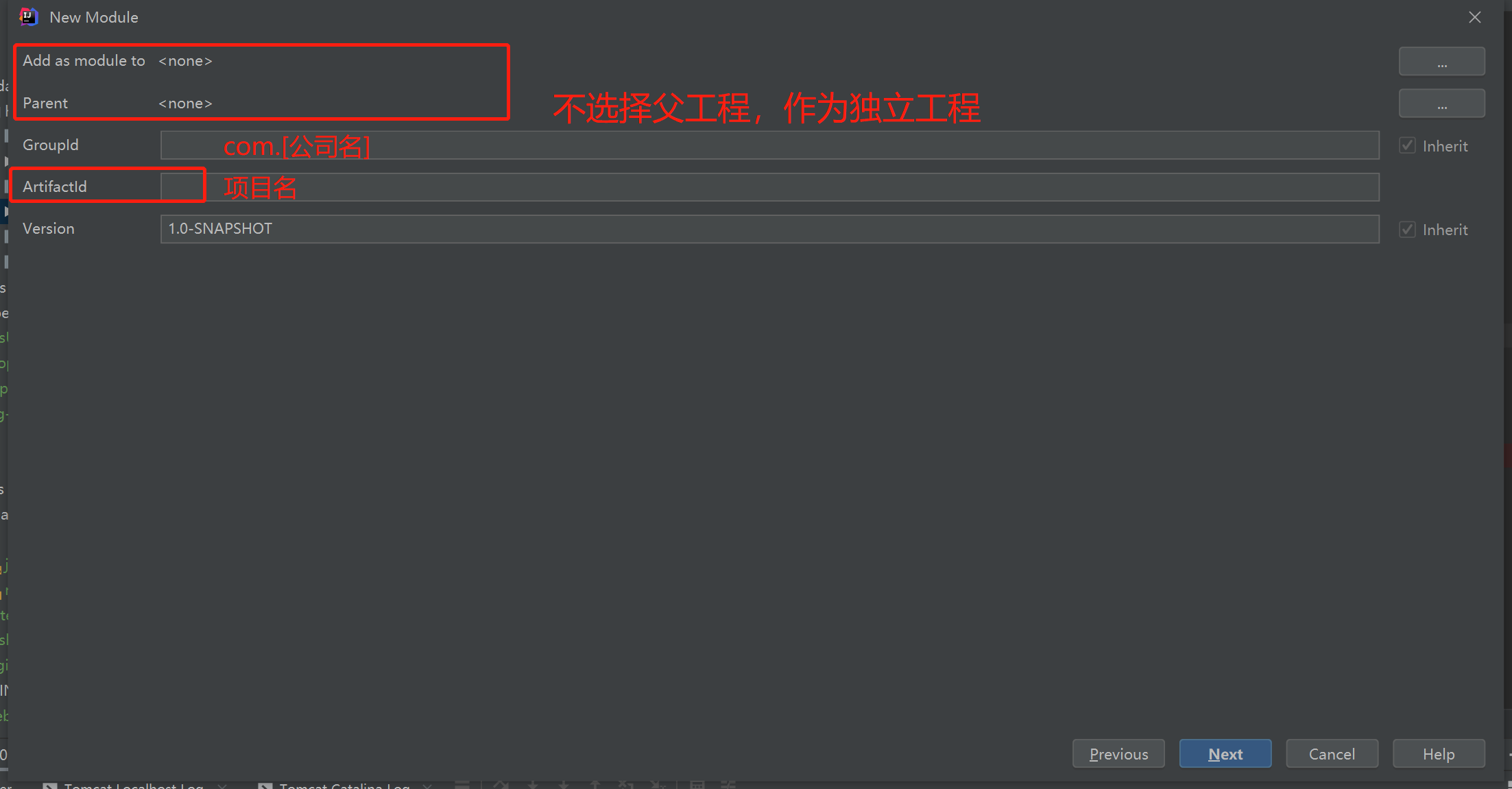
生成webapp资源路径
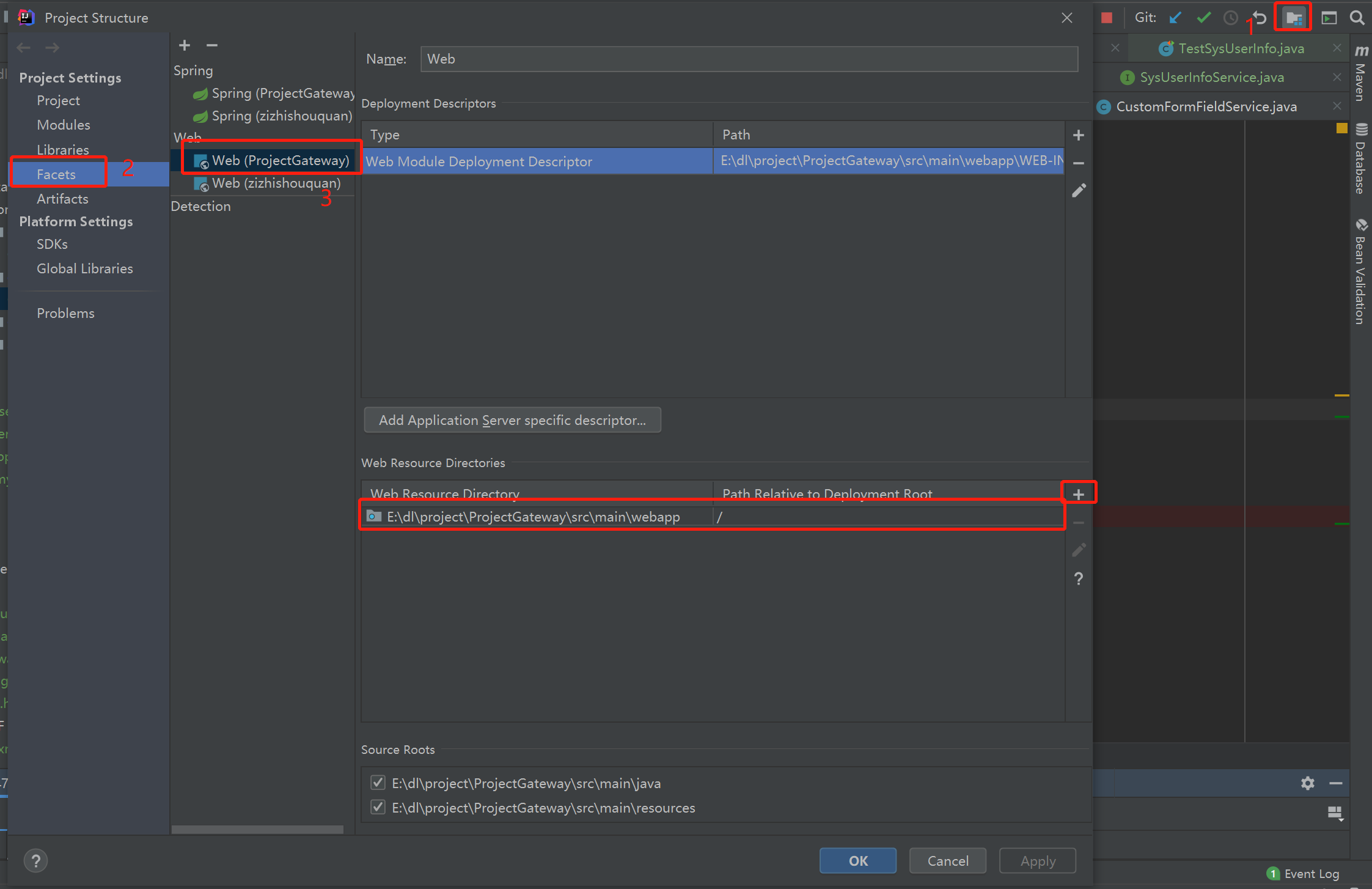
设置配置web项目配置文件web.xml
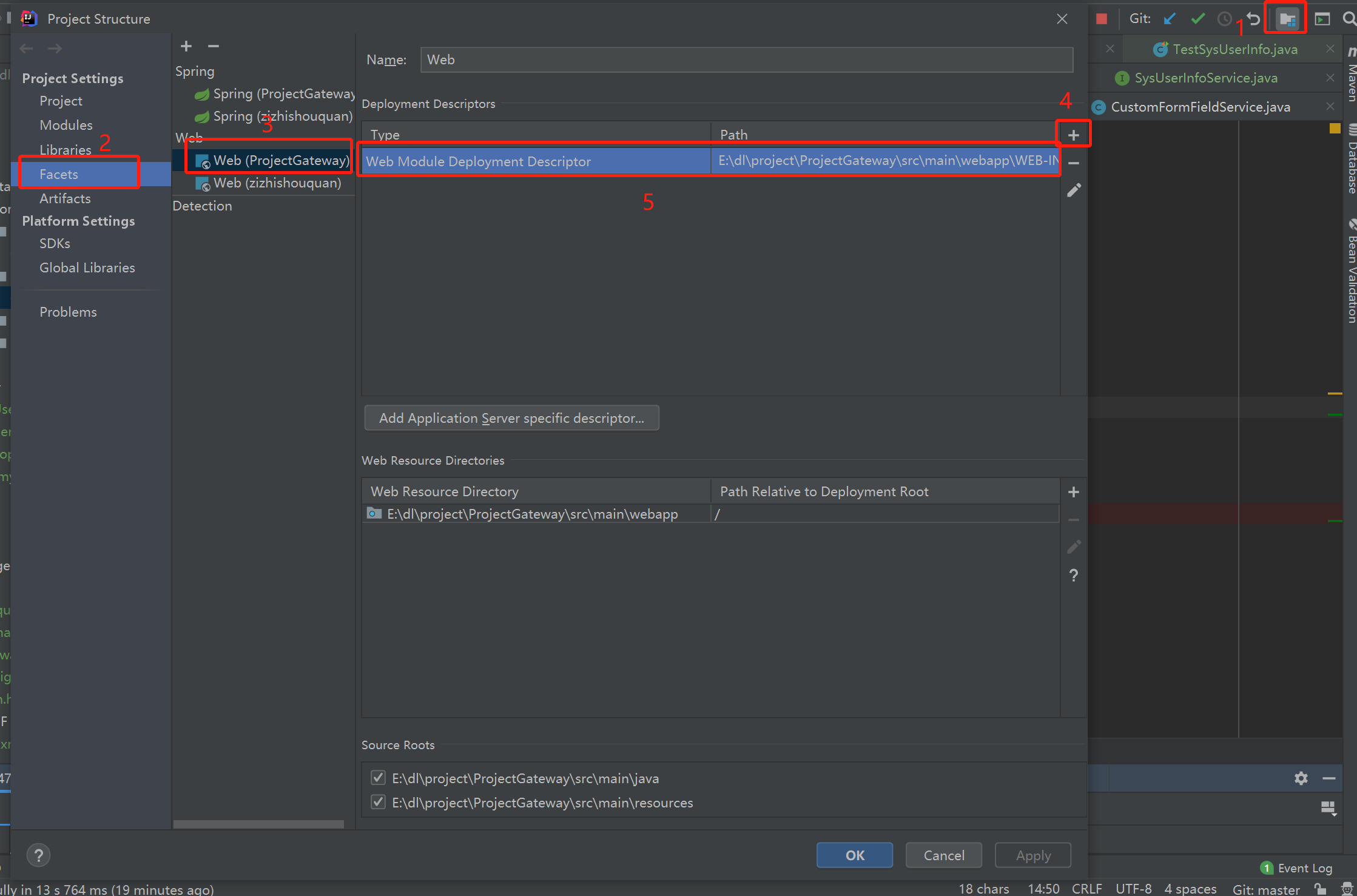
web.xml内容
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<!-- 加载spring容器 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:spring*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>spring和其他框架合并配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!-- 包扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.dldata.home.service.impl,com.dldata.home.dao"/>
<!-- 导入数据库配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<!-- 配置数据库 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 创建session工厂-->
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<!-- 告诉spring mybatis接口位置-->
<bean id="mapperScanner" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.dldata.home.dao"/>
</bean>
<!-- 事务管理-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven proxy-target-class="true" transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>




评论 (0)